A 1031 exchange, sometimes called a like-kind exchange or tax-deferred exchange, is a rule in the U.S. tax code. It lets real estate investors avoid paying taxes on profits when they sell one property and buy another that’s similar and worth as much or more. This helps investors keep their money working for them instead of paying it to the government.

How to Do a 1031 Exchange?
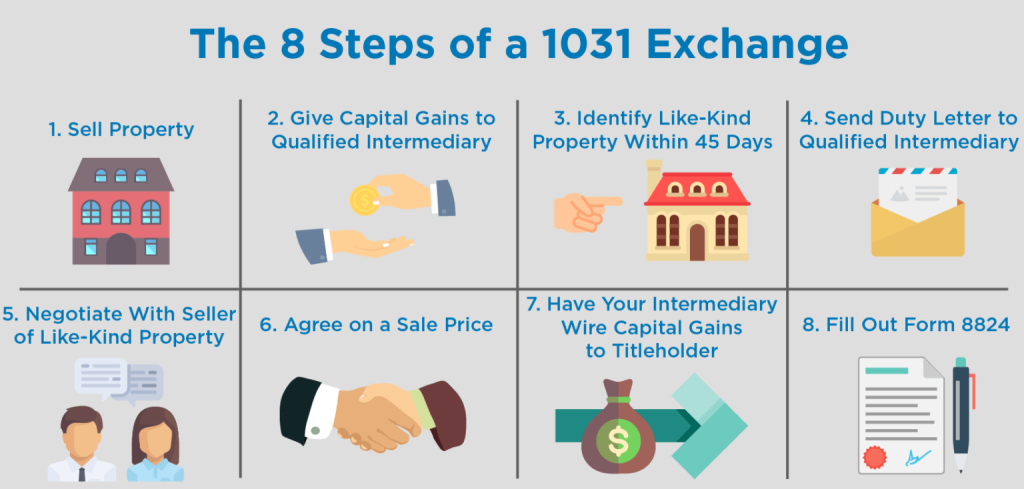
Step 1: Consult a Qualified Intermediary (QI)
The IRS says you have to use a Qualified Intermediary (QI) to do a 1031 exchange. A QI is a neutral third party who holds the money from the sale of your property and makes sure all the rules are followed. Find a trusted QI before you sell your property.
Step 2: Identify Replacement Properties
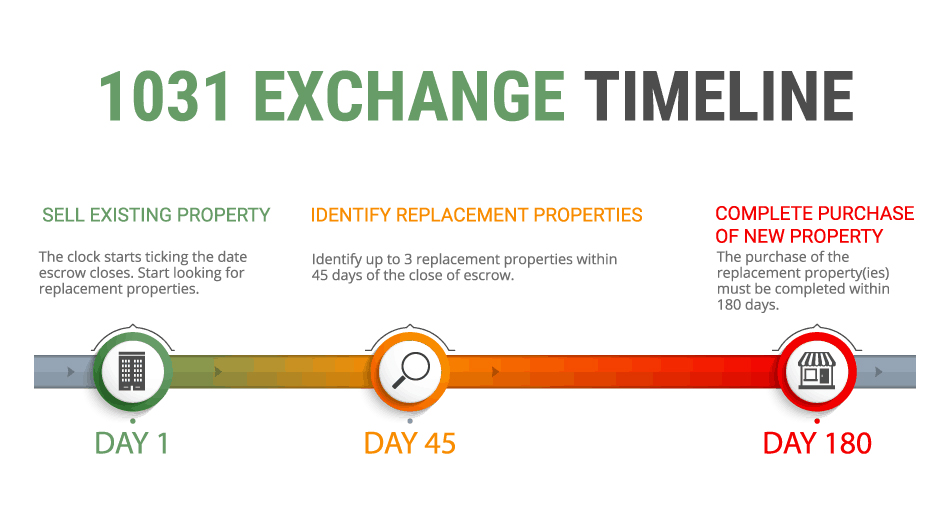
After selling your property, you have 45 days to choose your replacement properties. The IRS gives you three ways to do this:
- Three-Property Rule: You can pick up to three properties, no matter how much they’re worth.
- 200% Rule: You can pick as many properties as you want, but their total value can’t be more than 200% of the property you sold.
- 95% Rule: You can pick any number of properties, but you have to buy at least 95% of their combined value.
Step 3: Buy the New 1031 Exchange Property
You have 180 days from the sale of your old property to finish buying your new one. The new property must be worth at least as much as the one you sold. Also, all the money from the sale has to go through the QI.
Step 4: Keep Records and Report Everything
Make sure to document everything about your 1031 exchange. Work with your QI to fill out all the required forms and report the exchange on your tax return. If you miss any steps or paperwork, you might lose the tax benefits.
Why Use a 1031 Exchange?
- Delay Paying Taxes: You don’t have to pay taxes on your profits right away, so you can use all your money to buy new properties.
- Build Wealth: By reinvesting your profits, you can grow your real estate portfolio and buy bigger or better properties over time.
- Spread Out Your Investments: You can use a 1031 exchange to buy different types of properties or properties in different areas, which lowers your risks.
- Plan for the Future: A 1031 exchange can be part of your estate plan, helping you pass on valuable properties to your family while lowering their tax bills.
Conclusion
A 1031 tax-deferred exchange is a smart way to grow your real estate investments without paying taxes right away. By following the steps above and working with a Qualified Intermediary, you can take full advantage of this strategy.
Always talk to a tax expert or lawyer to make sure you’re following the rules. If done correctly, a 1031 exchange can be a key part of building a strong and tax-friendly real estate portfolio.
To learn more, check out the IRS fact sheet.
Curious about buying a fixer-upper? Check out this article to see if it’s worth the investment: https://chelsearowerealtor.com/buying-a-fixer-upper-is-it-worth-the-investment/


Recent Comments